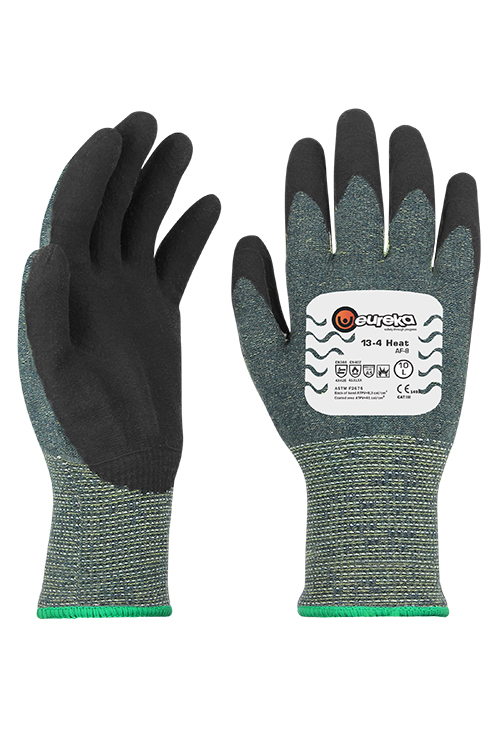
STANDARDS FOR PROTECTIVE GLOVES
» EN 407 » ASTMF2375 » EN 388 » EN 420 / EN ISO 21420 » ANSI CUT
Protective gloves are certified and tested according to different standards to provide the user with information so that the right glove with the right protection for the specific working area can be chosen.
Use gloves with Flame and Electric Arc protection correctly
When working with, for example, electricity and power generation, electrical maintenance, on the railways and in process industries, there is a risk of being exposed to Flash Arc.
The Electric Arc creates a massive heat radiation that can burn the skin. The hot air from the arc explosion can reach up to 10000°C, which poses a high risk of significant burns. The intense heat can ignite the glove, so it is important that the gloves protects against ignition and meltdown. The hands are one of the most exposed parts of the body when working with electricity.
Tranemo recommends:
- Use the gloves! Hands are the most exposed part of the body!
- Use dry gloves! Moist or wet gloves might cause steam that will reduce the protection significantly.
- Worn down gloves gives a reduced protection.
- Use clean gloves! The gloves are Flame Retardant but oil and dirt on the gloves might still burn, even though the glove are flame retardant.
- It is a good idea to bring an extra pair of gloves if one pair should be wet or dirty during the work day.
- Use the correct size! Good fitting gloves will reduce risk of entangling during work.
- Let other protective workwear overlap the gloves at the wrists.

EN 407
Protective gloves against thermal risks (and /or fire)
The standard is used for protective gloves which protect the hands against heat and/or flame; fire, contact heat, convective heat, radiant heat, small splashes or large quantities of molten metal.
Every risk that is tested gives a result divided into different levels and the symbol of the standard is supplemented with the terms below.
| Code | Explanation of term | |
| A | Burning behaviour | How flammable is the glove, does the material melt, how fast does the flame go out? Measure the time for an open flame and glow to extinguish after the source of ignition is removed, 1-4 (level 3 or 4 is classified as Flame Retardant) |
| B | Contact heat | The glove should insulate against contact heat and must not melt. The test measures the exposure to hot object with limited heating of hand during 15s, 1-4 (level 1=100°C, level 2=250°C, level 3=350°C, level 4=500°C) |
| C | Convective Heat | The glove should insulate against convective heat and prevent penetration of hot air or steam. The test measures the time for harmful heat penetration, 1-4 (4 is the highest level)* |
| D | Radiant heat | The glove can reflect or absorb heat radiation and the skin should be protected from impact. The test is calculated at 20 kW/m² and results in level1-4 (4 is the highest level)* |
| E | Small splashes of molten metal | Test with small splashes of molten metal, 1-4 (4 is the highest level)* |
| F | Large splashes of molten metal | Test with large splashes of molten metal, 1-4 (4 is the highest level)* |
*X indicates that the test is not performed.

ATPV value for protective gloves
Protective gloves tested to ASTM F2675, is performed to determine the Arc Rating (ATPV or EBT) of a glove.
IEC 61482-1-2, Box test
This Electric Arc test provides a pass or fail at the two below test settings:
APC 1 - 168kJ (4kA, 400V)
APC 2 - 320kJ (7kA, 400V)
The test is modified for gloves, as gloves are not included in this standard and test method.
EN 388
Protective gloves against mechanical risks
This standard defines the mechanical performance and relevant test of the protective glove. The glove is tested for abrasion resistance, cut resistance, tear resistance, puncture resistance and impact protection. Every risk that is tested gives a result divided into different levels and the symbol of the standard is supplemented with the terms below.
| Code | Explanation of terms | |
| A | Abration resistance | 1-4 (4 is the highest level) |
| B | Cut resisitance (coup test), optional older test | 1-5 (5 is the highest level) X indicates that the test is not performed |
| C | Tear resistance | 1-4 (4 is the highest level) |
| D | Puncture resistance | 1-4 (4 is the highest level) |
| E | Cut Resistance ISO 13997 | A-F (F is the highest level) A=2N, B=5N, C=10N, D=15N, E=22N, F=30N |
| F | Impact Protection | Indicated only if the test has been performed. P=achieved |
EN 420 / EN ISO 21420
Protective gloves – General requirements and test methods
This standard defines the general requirements and relevant test procedures for glove design and construction, resistance of glove materials to water penetration, innocuousness, comfort and efficiency, marking and information supplied by the manufacturer.

ANSI CUT
American standard for cut resistance
As a complement to the European standard Eureka use the ANSI test for cut recistance. This is to achieve a higher result span, A1-A9. The result is given in Newton. The test methods is the same as the ones in EN 388.

